How blockchain technology can disrupt the issuing and verification of digital badges for learning achievement.
Where do you store the certificates of your professional or academic achievement that you have earned throughout your career or school life? Framed on your wall, saved in your documents, on LinkedIn, or do you even remember where they were stored? Read more to learn about how microcredentials and blockchain can supplant the old system.
For many years, we have used degrees and diplomas to demonstrate our achievements or acquired skills; however, these constitute an outdated format that does not provide detailed information about what a person knows how to do or what they have learned.

With rapidly growing and changing industries, continuous learning has become essential to ensure current and prospective employees keep up with the latest trends. To meet these needs, educational providers have introduced partial accreditation, allowing people to take short, career-oriented courses at their own time and pace. Learners are thereby awarded with micro-credentials through digital badges which can be shared and verified online.

Micro-credentials are part of the larger trend of digital credentialing.
What are digital credentials?
Digital credentials are guides or graphic representations of achievement, knowledge, competencies, or skills. Digital credentials are distinguished from traditional paper addresses by four main characteristics:
- Portability. We can take the digital credentials anywhere because they live in the digital world.
- Verifiability in Real Time. This means that anyone can check the digital credentials. It’s different from a PDF, which is subject to falsification.
- High Density of Information. Digital credentials provide more information than we might find in a PDF because metadata includes detailed information about achievement such as:
Description of the learning experience– including course syllabi and other comprehensive information about the course(s).
List of specific skills acquired– including a list of skills as searchable ‘tags’ that recruiters and employers request that applicants have.
Criteria for awarding the certification– specifying what the students had to do to gain the achievement.
Evidence– publicly available evidence of the learning process through a link to the work the student has done (i.e. thesis, online portfolio, group project, etc.). - Sociability. Sharing credentials on social networks is a way to add more to our digital identity by making our achievements and professional or academic recognition visible.
Digital micro-credentials are more granular awards that are distributed as digital badges at different stages of a larger certificate/diploma/degree program or else awarded by employers or training centers to acknowledge achievement of specific learning outcomes.

The best known micro-credentialing framework is Open Badges since it can be implemented by anyone and provides the interoperability ensured by over 3000 partner organizations around the world that create and issue this type of digital micro-certificate.
Micro-credentials and digital badges have established themselves and are in wide practice already. So how does blockchain fit in?
What is blockchain?
Blockchain is an emerging technology that functions through a chain of blocks. Think of the analogy of a massive, public and decentralized ‘notary’, where any information that must be verified or authenticated can be done through blockchain technology. It is a larger part of the transition to web3.
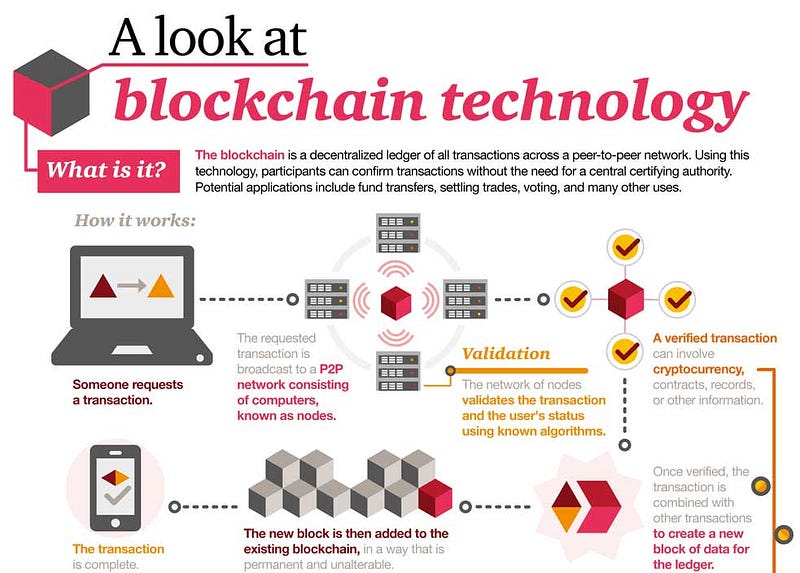
Benefits of blockchain for digital certificates
Blockchain technology supports the issuance of digital badges, and has great opportunity for use in education because it provides security by validating degrees and certifications registered on the blockchain while simultaneously allowing everything to be verified in real-time and accepted worldwide.
In short, blockchain technology provides decentralization, security, immutability, availability, and anonymity, all which can be leveraged for the issuance and verification of educational certifications.
ILS
Since micro-credentials are of short duration, rewards such as digital badges are frequently generated, so issuing and verifying micro-credentials can be time consuming; moreover, digital badges can be forged by users making them trust-less.
In 2019, the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) created the Verifiable Credential Model 1.0 standard. This not only standardizes certification exchange at the national level, but also ensures that digital diplomas and electronic documents are recognized and banned worldwide. Blockchain technology enables this standard to be implemented with a higher degree of security, trust, interoperability and robustness than any other solution that uses traditional technologies.
Current developments of blockchain microcredentials
The popularity of blockchain continues to increase and applications beyond the financial field are being developed.
- University of Mauritius has detailed a micro-credential system consisting of quizzes and digital badges was built with Ethereum blockchain together with IPFS to store the badge image and firebase for examination, registration, and storing courses. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666285X21000546#bib0011
- Forward Protocol has deployed smart contracts on Polygon (Matic) to debut a blockchain-based learning system for a blockchain-enabled audience (English Forward (EnglishForward.com) the internet’s largest ‘learn English’ Q&A site) with the vision of providing a democratic, sustainable, and self-applied learning system that operates without middlemen and central authorities. https://forwardprotocol.medium.com/forward-protocol-and-polygon-the-sweeping-influx-of-decentralized-education-users-33c460e3eddc
- Hyland Credentials offers a complete system to issue digital credentials in a blockchain-secured format that is easily shareable and instantly verifiable anywhere in the world. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/sites/6893d95a-en/index.html?itemId=/content/component/6893d95a-en
- BCDiploma has created the first 100% blockchain Open Badge for forgery-proof, durable micro-credentials. Ontario universities, IFOCOP and emlyon executive education use this latest-generation format. https://www.bcdiploma.com/en/microCertification
- University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa performed qualitative research in their own blockchain-based micro-credential management system and found that qualitative evaluation reveals that such systems can decrease the overall cost and administrative workload. https://scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/d72a8b0a-e74a-42da-a6a0-1a5172b4866b
More research is needed surrounding microcredentials and blockchain for education.
While the issuers see the implementation as beneficial and low-risk, general knowledge about the blockchain and its advantages, especially in the context of managing micro-credentials, is insufficient. This, among other challenges, must be addressed before widespread adoption of blockchain-based micro-credentials can be achieved.
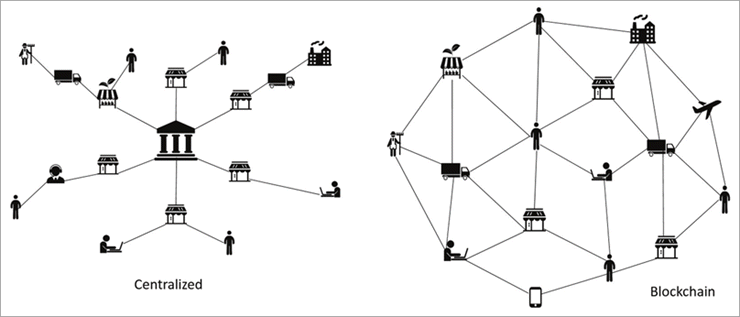
Blockchain technology is slowly but surely changing the world. Cryptocurrencies have a profound impact on the economic and technological landscape. With the emergence of COVID-19, the education sector, just like other sectors, needs a complete overhaul or redesign to continue to produce graduates who are able to contribute effectively to an ever-changing world.
Thank you for reading about Microcredentials and the Blockchain. Please share this article with your learning and teaching networks.
Book a Consultation: https://www.icarus.so/contact
Follow us on Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/IcarusLS
Follow us on LinkedIN: https://www.linkedin.com/company/icaruslearning
